RI DD Rate Review: "Refresh" Or "New Analysis" of Project Sustainability?
/By Gina Macris
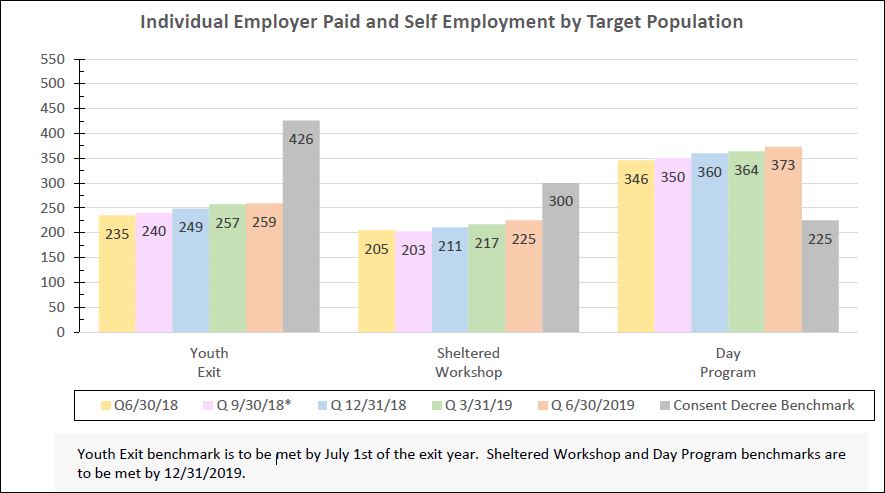
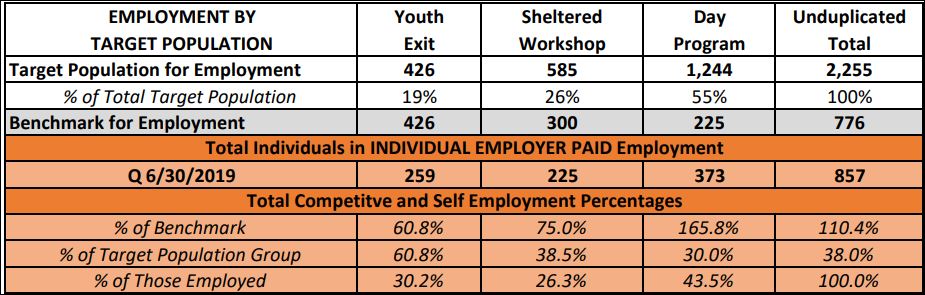
Under court order, Rhode Island is conducting a comprehensive review of how it provides services for adults with developmental disabilities – a study that could have a profound effect on the quality of their lives.
Will the rate review go far enough to realize the goal of a 2014 consent decree – a system of services individualized enough to enable persons with developmental disabilities to become integrated in their communities?
In seeking a consultant for the rate review, the state said it wanted to “shift toward a system of community based supports that promote individual self-determination, choice and control.”
In the end, the state’s evaluation committee selected the firm that offered “more a refresh of a prior model than a new analysis,” Health Management Associates, the parent company of Burns & Associates (HMA-Burns). Under an independent corporate structure more than a decade ago, Burns & Associates helped the state create the problematic reimbursement system now in place, called Project Sustainability.
With completion of the study not expected until December, it’s too early to tell what the final recommendations might look like.
But the selection process suggests the state does not want to stray too far from the structure of Project Sustainability.
One of the three finalists for the rate review, Guidehouse Inc., said as much in its proposal:
“Guidehouse assumes in our proposed approach that BHDDH is not looking for an overhaul of those mechanisms now in place.”
While there have been some changes in Project Sustainability, a federal judge has found that that some of its features amount to administrative barriers to the system of individualized, integrated services required by the 2014 consent decree.
Those barriers, which are expected to be addressed in rate review, include
A lack of individualized budgeting
Exhaustive documentation of staff time with each client that detracts from services and is a costly burden for providers
Staffing ratios that make integration in the community challenging
The state scored five bidders in two categories. Before cost could be considered, a four-member committee conducted a technical evaluation, valued at 70 percent of the overall score, which determined how closely the submissions matched objectives of the state’s request for proposals. Three firms, Guidehouse, Milliman and HMA-Burns exceeded the minimum of 60 points to be considered finalists.
HMA-Burns scored 61 points in the technical evaluation, one more than the 60 points necessary to qualify.
The evaluation committee found the HMA-Burns approach was “clearly defined, and the data approach is strong. However the methodology seems more a refresh of a prior model than a new analysis.” The proposal also “has a continuation of ‘buckets’ for funding rather than a robust approach to individual budgeting,” the committee said.
By comparison, the committee said Guidehouse, the top scorer, had an “engaging proposal, well written, visually engaging with good content.” There was also a “wide range of relevant experience, including recent experience assessing self-direction. (families and individuals designing their own service programs.)”
Among other things, the committee noted that Guidehouse had a “good understanding” of supplementary needs assessments that could lead to more accurate budgeting and reduce appeals that have resulted in the award of millions of dollars annually for supplemental services to which adults with developmental disabilities were entitled.
The cost proposals counted for 30 percent of the overall evaluation, but the committee did not score the originals from the three finalists. The original bids were:
HMA - $339,680 - 1,516 hours
Guidehouse - $499,350 - 2,235 hours
Milliman - $1,203,181 - 4,628 hours
In its evaluation memo, the committee expressed concern that the bids reflected too much of a variation in the effort that would be devoted to the project. It did not interview the vendors, a common practice among public purchasing officials.
Instead, the committee asked for a second round of bids for a project that would encompass 3,000 hours, which the committee said would be sufficient to complete the rate review.
The results:
HMA- $490,875
Guidehouse - $670,290
Milliman - $773,4000
After the second round of bidding, HMA-Burns tied with Guidehouse in the overall scoring but remained the lowest bidder. The final decision was made on the basis of cost.
ISBE MEANS A SMALL BUSINESS ENTERPRISE OWNED BY AT LEAST ONE PERSON WHO IS A WOMAN, MINORITY OR HAS A DISABILITY
During two meetings encompassing the evaluation process, the four-member committee awarded a single score in each category for each proposal through a collective group decision, or consensus, rather than individual scoring.
Individual, independent scoring is recommended as a “best practice” by the Center for Procurement Excellence. The Center is a non-profit organization that promotes education and training of pubic procurement officers and excellence in solicitation practices.
Members of the evaluation committee were Kevin Savage, Director of the Division of Developmental Disabilities; Anne LeClerc, Associate Director of Program Performance at BHDDH; Marylin Gaudreau, Data Analyst II at BHDDH, and Ashley Bultman, Senior Economic & Policy Analyst in the Office of Management and Budget at the Department of Administration.
In the end, the second round of bidding narrowed the range between the lowest and highest cost proposals but their relative positions didn’t change. Nor did the evaluation committee gain any additional information about the differing approaches.
In their cover letters with the second bids, both HMA and Guidehouse reiterated that they believed the work could be done in less than 3,000 hours.
Milliman, on the other hand, stated again that it believed the rate review would take more time. In fact, the letter said that if they were chosen, they would have to revise their technical proposal to conform with 3,000 hours’ work.
Gomes, the DOA spokesman, said purchasing rules gave the committee the choice of scoring proposals individually and interviewing the finalists, but he did not say why the committee did not do so.
Asked whether the evaluation process was designed to steer the project to a refresh of Project Sustainability instead of a new analysis of the system, Gomes said: “The goal of a competitive bid is to retain the best services at the most competitive price.”
“The request for proposals process evaluates both the technical aspects of the proposal and the submitted cost,” he said.
“When there is a wide discrepancy in the cost proposals, the Division of Purchases and agency initiating the procurement will provide an estimated level of effort (i.e. number of hours needed to complete the scope of work) and ask the respondents to submit a best-and-final offer.”
He said a “best and final offer process” is described in state Rules and Regulations 220-RICR-30-00-6(D) and state law R.I. Gen. Laws § 37-2-20(b) read in conjunction with state law R.I. Gen. Laws § 37-2-19(d) and (e).