RI DD Officials "Trying To Do The Right Thing," Says Judge In Review of 2014 Olmstead Consent Decree
/By Gina Macris
Rhode Island’s efforts to implement a 2014 consent decree to help adults with developmental disabilities become part of their communities won plaudits from a federal judge July 28, althougth some officials indicated there’s still a long way before the changes permeate the system of state services.
Judge John J. McConnell, Jr. said he is heartened “when a state entity is trying to do the right thing. It’s not the case where the state is acting in any way in bad faith.”
“Compared to about a year ago we are in a very different place,” he said.
In May, 2016, McConnell issued a 8-page order warning the state he would entertain contempt proceedings unless it moved forward with implementation of the consent decree, which at that time had been stalled for two years.
At the latest hearing, July 28, McConnell said there had been “positive movement” in the state’s efforts to carry out the requirements of the consent decree and urged state officials to “keep it up.”
The judge acknowledged that sweeping changes in the leadership of state agencies responsible for the disabilities programs in recent months had left him feeling “quite nervous” about the state’s ability to comply with his orders, but he said “now it doesn’t feel that way at all.”
McConnell chose a relatively informal setting for the hearing, convening his review not in his courtroom but in the richly paneled library of the Beaux Arts federal building on Kennedy Plaza in Providence, and inviting participants around a conference table to remove their jackets.
A lawyer for the U.S. Department of Justice, Nicole Kovite Zeitler, and an independent court monitor, Charles Moseley, cited advances in the handling of bureaucratic issues that are pre-requisites for a turn-around in the system that will take years to accomplish. The areas they covered included:
- The realignment of social work staff to better oversee changes in the way services are delivered
- Additional steps intended to lay the foundation for an active, multi-faceted quality improvement effort involving the state Department of Behavioral Healthcare, Developmental Disabilities and Hospitals (BHDDH) and the Office of Rehabilitation Services (ORS)
- Improved communication with service providers, and with the publicThe expanded availability of training and information on the principles of individualized planning and personal choice that are at the heart of the consent decree – and the federal law behind it.
There were, however, signs that, for some individuals who depend on developmental disability services, change has not yet arrived.
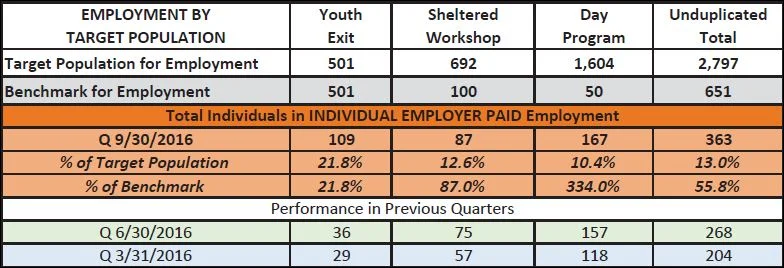
For example, Zeitler said that of 22 private agencies participating in a pilot program to encourage job-placements, 42 percent –nearly half - say they can’t take new clients.
Moseley said he “regularly” gets reports from families who say that they have been turned down by service providers they sought out.
Although the pilot project in supported employment is billed as an “incentive” program, participating agencies report privately they operate at a loss for each client they place in a job.
The legislature allocated $6.8 million for supported employment in the fiscal year which ended June 30, but the pilot program did not begin operations until January, and in the first six months it paid out a total of about $122,000 to participating agencies, according to BHDDH calculations obtained by Developmental Disability News.
Rebecca Boss, the BHDDH director, acknowledged there are “challenges” to delivering those supported employment services but did not elaborate. A report from Moseley to the judge submitted the day before the hearing said there have been multiple meetings between state officials and the providers to discuss various factors affecting the supported employment program, including “operational issues that are reported to be impeding the ability of the organizations to meet their placement goals.”
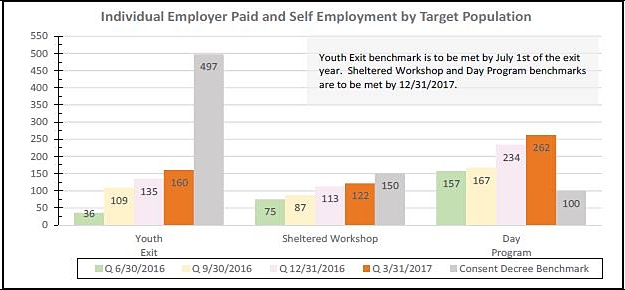
McConnelland the consent decree officials at the table spent considerable time discussing a relatively low employment rate of young adults – the very group most likely to have had the broadest experiences in high school, including school-to work internships.
The participants acknowledged that the employment rate for that group, 32 percent, was artificially depressed, because the number of individuals in the young adult category has grown dramatically, from 151 to 497, in the last nine months. It takes time to find the right job, Zeitler said.
But the monitor said in his latest report to the judge that progress in finding jobs for young adults “has been slow.” Even if one analyzes only the original 151 young adults and discounts 60 of them who are not receiving BHDDH services, the employment rate is 51 percent, Moseley said in the report.
He recommended that the state contact each of the 60 not receiving services to make sure they know that supports are available if they need them.
Clients recently interviewed by Zeitler and DOJ colleagues said they were sometimes “bored” with their daytime non-work activities, Zeitler reported. The Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA) says persons who receive public supports must have personal choice in deciding what they do with their time, both for work and leisure.
But the way resources are currently invested does not necessarily promote “inclusivity,” noted Boss, saying the department is hoping to do some “rebalancing” of the way money is spent.
The individual choice mandated in the consent decree implies one-to-one or small group staffing, assuming that a few friends want to do something together in the community. But a fairly rigid regulatory structure currently in place doesn’t allow for such staffing unless clients are deemed to have extensive disabilities.
The Division of Developmental l Disabilities is in the process of rewriting all its regulations to change from a system that assigns funding based on the severity of a disability to one that stresses individualization and personal choice, or“person-centered planning,” in accordance with the ADA and the consent decree.
As Moseley noted, the state must make these changes anyway to comply with the broader federal Medicaid Home and Community Based Rule (HCBS). The federal-state Medicaid program pays for all developmental disability services in Rhode Island.
Like the consent decree, HCBS derives its authority from the 1999 Olmstead decision of the U.S. Supreme Court. The Olmstead decision re-affirmed Title II of the ADA, which emphasizes its primary purpose to integrate those with disabilities into the mainstream of society and respects their individual choices on the degree to which they wish to participate.
The last time BHDDH attempted regulatory reform along similar lines, in 2015, an internal BHDDH work group came up with recommendations that would have cost tens of millions of dollars. The proposed changes did not move forward.
In his most recent report to the judge, Moseley said that the effort to gain greater flexibility over existing funding “is a positive move, but additional steps need to be taken to map out a process for ensuring that funding supports integrated person-centered day services” that meet the standards of the consent decree.
Zeitler said management officials of direct service agencies seem to understand the principles of individualized, or “person-centered” activity plans, but some direct care workers “don’t speak the language.”
Zeitler suggested that more training is in order. Although the training is available, tuition-free, Kerri Zanchi, developmental disabilities chief at BHDDH, indicated there was no “quick fix” to this problem, given the high turnover in the workforce.
Zeitler, meanwhile, praised the way Zanchi has moved around staff to make the most of available personnel, calling the reorganization “very creative.”
Zanchi has added four workers to the case management unit, reducing caseloads from 205 to 152 per person. Two of the workers came from the unit that determines eligibility for services and two came from a separate group that assesses the support needs of clients once they are found eligible for services.
Another worker has been tapped to serve in the newly created position of transition coordinator, to serve teenagers and young adults moving from high school to adult services. The Division of Developmental Disabilities has hired a new residential coordinator to address housing options for those who do not live with their families.
An outside quality improvement expert enlisted by Moseley has said in a report that "there is a significant commitment to change" at BHDDH and ORS to ensure high program standards are implemented across the board.
"But the staff available to implement change are stretched very thin," wrote Gail Grossman in a report that is part of Moseley's latest filing with the court. Grossman continued: "Serious consideration needs to be given to the need for additional staff resources if DDD (the Division of Developmental Disabilities) and BHDDH are going to develop, manage and oversee a strong QMIS (Quality Management and Improvement System) structure."
BHDDH has a unit entitled quality improvement, but its scope is limited to investigations of neglect or abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Click here for the monitor's latest report to the judge.
Related articles: Judge Willing To Intervene In RI Budget Impasse
Supported Employment Program Falls Short Of Initial Goals in RI