RI Senate Finance Hearing Highlights Cost Overruns, Challenges, in DD Budgets
/By Gina Macris
Cost overruns are a recurring theme for Rhode Island’s Division of Developmental Disabilities, with expenses for mandated services running about $4.4 million over budget in the current fiscal year, while $6 million in projected savings group home-related costs are proving elusive.
Overall, Governor Gina Raimondo seeks to close out the current fiscal year with a total of $250.6 million in developmental disabilities funding and requests $256.7 million for the fiscal year beginning July 1. Taken together, the $4.4 million increase she has requested in current spending and the proposed increase of nearly $6.1 million for the next fiscal year run almost $10.5 million more than the existing budget authorized by the General Assembly - $246.2 million.
At a budget hearing April 4, members of the Senate Finance Committee seemed to understand the challenges faced by the Department of Behavioral Healthcare, Developmental Disabilities and Hospitals (BHDDH), but Sen. Louis DiPalma, D-Middletown, still asked officials for more realistic budget figures in the future.
One case in point was $100,000 in actual savings in costs related to group homes, rather than the $2.6 million cut in state revenue that originally had been projected during the current fiscal year.
The savings are associated with a shift in residential care from group homes to less costly shared living arrangements in private homes scattered throughout the state, a change that is driven both by budgetary constraints and federal Medicaid rules.
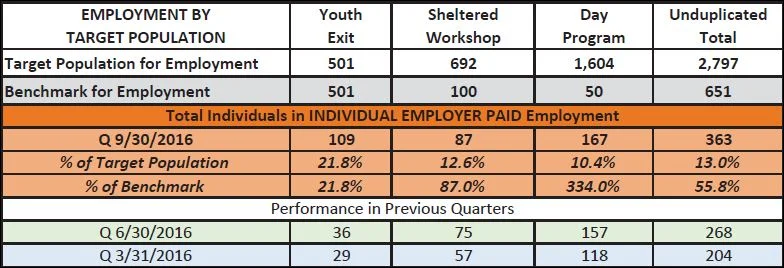
In April of 2016, BHDDH said it would move a total of 100 individuals with developmental disabilities from group homes to shared living by the end of the fiscal year June 30, but it achieved only 27 transfers, DiPalma said.
For the current fiscal year, the goal is 66 moves. Noting the $2.5 million gap between projected and actual savings, DiPalma said he would have recommended a target of 45 transfers.
But “the budget is what it is,” he said.
“If you want to move someone, they have to say yes,” DiPalma said. “If they say no, they stay where they are.”
Rebecca Boss, the acting BHDDH director, said, “you are right about the challenges.”
But she added that BHDDH already has 45 commitments from group home residents who have agreed to go into shared living.
A year ago, the Division of Developmental Disabilities had not yet done a “deep dive” into the shared living program to understand what needed to be done to make it more attractive to consumers, Boss said. She suggested that since then, officials have identified some issues that have prevented more rapid expansion of the program, but Boss was not specific.
Pressed for more details, she said they would be forthcoming in a month – May 5. At last count in December, there were 333 residents in shared living arrangements and 1,283 in state or privately-run group homes, according to a Senate fiscal analysis.
In the next budget, beginning July 1, BHDDH has proposed saving $3.9 million in state revenue related to movement out of group homes, but Boss said she could not guarantee that the department would meet its future budget targets.
DiPalma also warned Boss that a similar transition away from group home care for children in state custody has shown that, for a time, residential costs actually increase because the state must maintain group housing while it builds its community-based network of home care.
A big part of the savings plan in the next fiscal year is to close a total of five group homes run directly by the state through Rhode Island Community Living and Supports (RICLAS), a division of BHDDH, including two in July, one in October, and two in January, 2018.
Jim Cenerini, legislative affairs and political action coordinator for the American Federation of State, County and Municipal Employees, Council 94, (AFSCME) expressed concern about the closures, which would move 30 residents, or 20 percent of the 150 people in the state-run system, into private care.
He said BHDDH officials have not talked about the closings with the union, which represents several hundred workers staffing the homes.
Boss said BHDDH officials would be “more than happy” to sit down with the union.
Cenerini said, “We believe RICLAS provides a very vital service as a provider of last resort.” He maintained that RICLAS residents are not ready to go to shared living arrangements.
Two years ago, the union negotiated many cost-saving concessions with BHDDH that gave the department much more flexibility in staffing, but BHDDH hasn’t implemented any of the reforms except to hire seasonal workers who are ineligible for benefits, Cenerini said.
RICLAS workers are state employees, many of whom make at least double the poverty-level wages of workers in a parallel system of private agencies under contract with the state to provide most of the developmental disability services.
DiPalma told Cenerini that the “train has left the station” on the shift from congregate care to settings that are more like home.
The change in Medicaid rules have been influenced by the 1999 Olmstead decision of the U.S. Supreme Court, which ruled that the Americans With Disabilities Act requires services for all people with disabilities to be available in the least restrictive environment that is therapeutically appropriate. That environment is presumed to be the community for both daytime and residential services.
“It’s up to us to figure out how to move those people into the community,” DiPalma said, and “how to facilitate the workers at RICLAS to do other things.” The conversation should not be about residents remaining in RICLAS homes “because this is what we have,” DiPalma said.
Cenerini emphasized that RICLAS offers continuity of care, something the private system lacks because of low wages and high turnover. “I don’t want to see the destruction of my union,” he said.
About 20 RICLAS workers also host adults with developmental disabilities in their homes as shared living providers, Cenerini said.
One reason BHDDH has a hard time meeting budget targets, Cenerini said, is that “they are asked to do so much with so little.”
Testimony at the hearing reiterated support for a $6 million wage increase in the fiscal year beginning July 1 for private-sector direct care workers, who now earn an average of about $11.14 an hour, according to the latest figures provided by Donna Martin, executive director of the Community Provider Network of Rhode Island.
The current hourly average of $11.14 is only slightly higher than the federal poverty level of $9.82 an hour for a single parent household with two children, a profile that represents the typical direct care worker in developmental disability services, she said.
About one in three workers a year leave private agencies, many of them for slightly higher pay in a local market or to work at RICLAS, where they are paid an additional $5 an hour to do the same work, Martin said in written testimony she submitted to the committee.
The budget now in effect gave private-sector workers their first increase in a decade, putting an additional 36 cents an hour in their pockets, before taxes.
DiPalma has sponsored a resolution that would increase the pay of these workers to $15 an hour in five years – the fiscal year beginning July 1, 2021. (In the House, State Rep. Teresa A. Tanzi has sponsored a similar resolution, which would achieve a $15 hourly rate in three years – by July 1, 2019.)
DiPalma’s and Tanzi’s resolutions also urge the legislature to link future annual raises to the consumer price index so that pay stays ahead of the minimum wage, currently $9.60 an hour. Governor Raimondo has proposed increasing the minimum wage to $10.50 on July 1. The Senate Finance Committee held a separate hearing on wage increases May 21. (Click here to read related article.)
DiPalma highlighted another feature of the budget that seeks to add a total of $500,000, or $250,000 in state funds, to a supplemental allocation for developmental disability services that he said runs about $20 million to $22 million annually.
These supplemental funds are used when those receiving developmental disability services believe their individual budgets are inadequate and make a successful argument for more money, or when they need a short term boost in care triggered by events like a discharge from a hospital, according to Kerri Zanchi, Director of the Division of Developmental Disabilities.
DiPalma said he concurred with the use of funds to cover short-term extra needs, but he believed $22 million a year, or 10 percent of all service appropriations - was too high for supplemental appropriations.
He called on BHDDH to change the equation that assigns individual funding.
Zanchi said the individual budgets are assigned on the basis of a standardized assessment of an individual’s need called the Supports Intensity Scale. In November, Rhode Island moved to an updated version of the assessment believed to be more accurate and began tracking the results to see if the number of appeals decline in the long run.
DiPalma noted that the current arrangement favors those who have the strongest advocates on their behalf.
Another hearing on budget is scheduled before a subcommittee of the House Finance Committee on Tuesday, April 11, in Room 35 of the State House at the conclusion of that day’s full House session.